Upload Images to Django Using Put Request
Prerequisite – Introduction to Django
In nigh of the websites, we often deal with media data such every bit images, files etc. In django we can deal with the images with the help of model field which is ImageField.
In this article, we have created the app image_app in a sample project named image_upload.
The very first step is to add below code in the settings.py file.
MEDIA_ROOT = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'media' )
MEDIA_URL = '/media/'
MEDIA_ROOT is for server path to shop files in the reckoner.
MEDIA_URL is the reference URL for browser to access the files over Http.
In the urls.py we should edit the configuration like this
from django.conf import settings from django.conf.urls.static import static if settings.DEBUG: urlpatterns += static(settings.MEDIA_URL, document_root=settings.MEDIA_ROOT)
A sample models.py should be like this, in that we have created a Hotel model which consists of hotel name and its prototype.
In this projection nosotros are taking the hotel name and its image from the user for hotel booking website.
class Hotel(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length = l )
hotel_Main_Img = models.ImageField(upload_to = 'images/' )
Hither upload_to volition specify, to which directory the images should reside, past default django creates the directory under media directory which will exist automatically created when we upload an image. No need of explicit creation of media directory.
We accept to create a forms.py file under image_app, hither nosotros are dealing with model course to brand content easier to understand.
from django import forms
from .models import *
class HotelForm(forms.ModelForm):
class Meta:
model = Hotel
fields = [ 'name' , 'hotel_Main_Img' ]
Django will implicitly handle the form verification's with out declaring explicitly in the script, and it volition create the coordinating form fields in the folio according to model fields nosotros specified in the models.py file.
This is the advantage of model class.
Now create a templates directory under image_app in that we have to create a html file for uploading the images. HTML file should look similar this.
<!DOCTYPE html>
< html lang = "en" >
< head >
< meta charset = "UTF-viii" >
< title >Hotel_image</ title >
</ head >
< body >
< form method = "post" enctype = "multipart/form-data" >
{% csrf_token %}
{{ form.as_p }}
< push button type = "submit" >Upload</ push button >
</ form >
</ body >
</ html >
When making a Postal service request, nosotros have to encode the data that forms the body of the request in some way. So, we take to specify the encoding format in the form tag. multipart/form-data is significantly more than complicated but it allows entire files to be included in the data.
The csrf_token is for protection confronting Cantankerous Site Request Forgeries.
form.as_p simply wraps all the elements in HTML paragraph tags. The reward is non having to write a loop in the template to explicitly add HTML to surround each championship and field.
In the views.py under image_app in that we have to write a view for taking requests from user and gives back some html page.
from django.http import HttpResponse
from django.shortcuts import render, redirect
from .forms import *
def hotel_image_view(request):
if request.method = = 'Postal service' :
form = HotelForm(request.Mail, asking.FILES)
if form.is_valid():
form.save()
return redirect( 'success' )
else :
form = HotelForm()
render render(request, 'hotel_image_form.html' , { 'form' : form})
def success(request):
return HttpResponse( 'successfully uploaded' )
whenever the hotel_image_view hits and that request is Mail, nosotros are creating an case of model form form = HotelForm(request.POST, request.FILES) image will be stored under request.FILES i. If information technology is valid relieve into the database and redirects to success url which indicates successful uploading of the image. If the method is not POST we are rendering with html template created.
urls.py will await like this –
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from django.conf import settings
from django.conf.urls.static import static
from .views import *
urlpatterns = [
path( 'image_upload' , hotel_image_view, name = 'image_upload' ),
path( 'success' , success, name = 'success' ),
]
if settings.DEBUG:
urlpatterns + = static(settings.MEDIA_URL,
document_root = settings.MEDIA_ROOT)
At present make the migrations and run the server.

When we hit the URL in the browser, in this style it looks.

Later uploading the image it will prove success.

Now in the project directory media directory volition exist created, in that images directory will be created and the image will exist stored under it. Here is the final outcome.
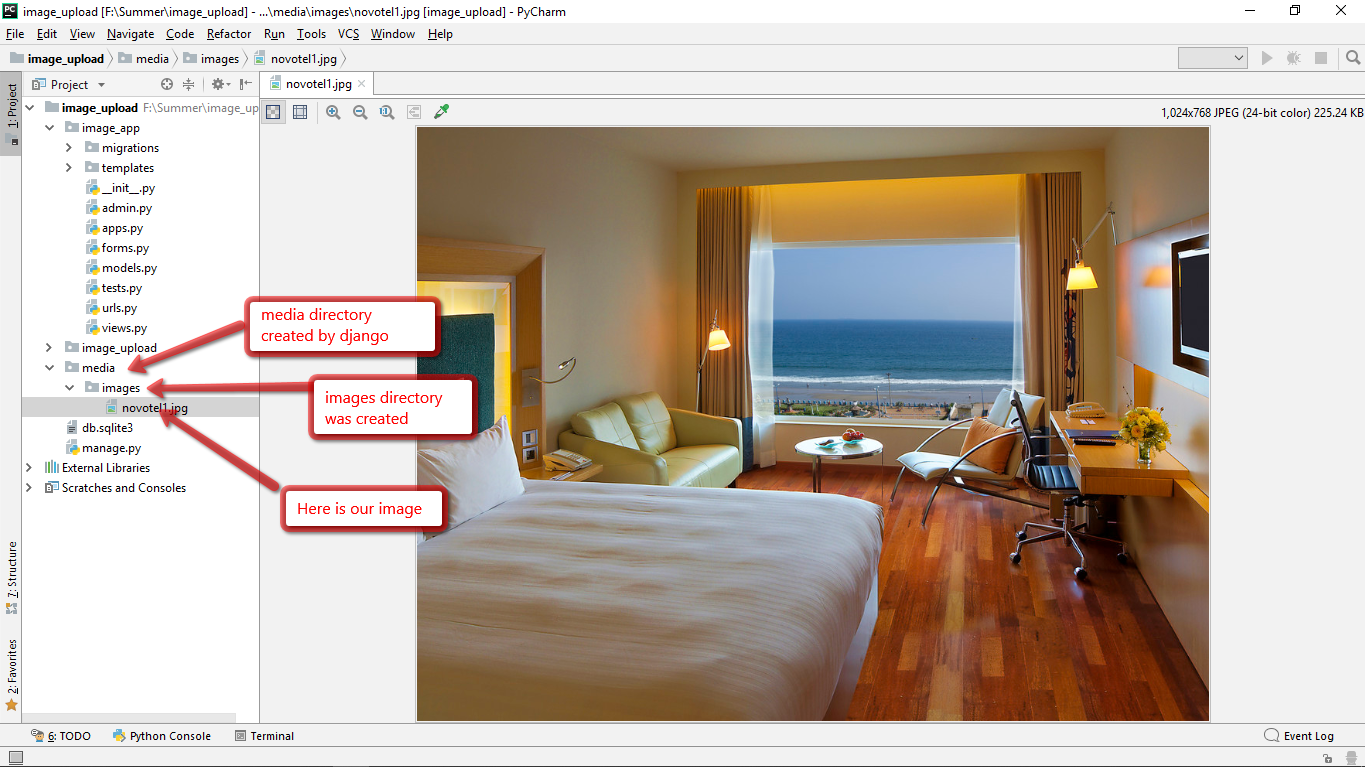
Final output stored in the database
Now we can write a view for accessing those images, for simplicity let's take example with one image and it is likewise applicative for many images.
def display_hotel_images(asking):
if request.method = = 'Become' :
Hotels = Hotel.objects. all ()
render render((request, 'display_hotel_images.html' ,
{ 'hotel_images' : Hotels}))
A sample html file template for displaying images.
Insert the url path in the urls.py file
# urls.py path('hotel_images', display_hotel_images, proper noun = 'hotel_images'), Here is the final view on the browser when nosotros endeavor to admission the paradigm.
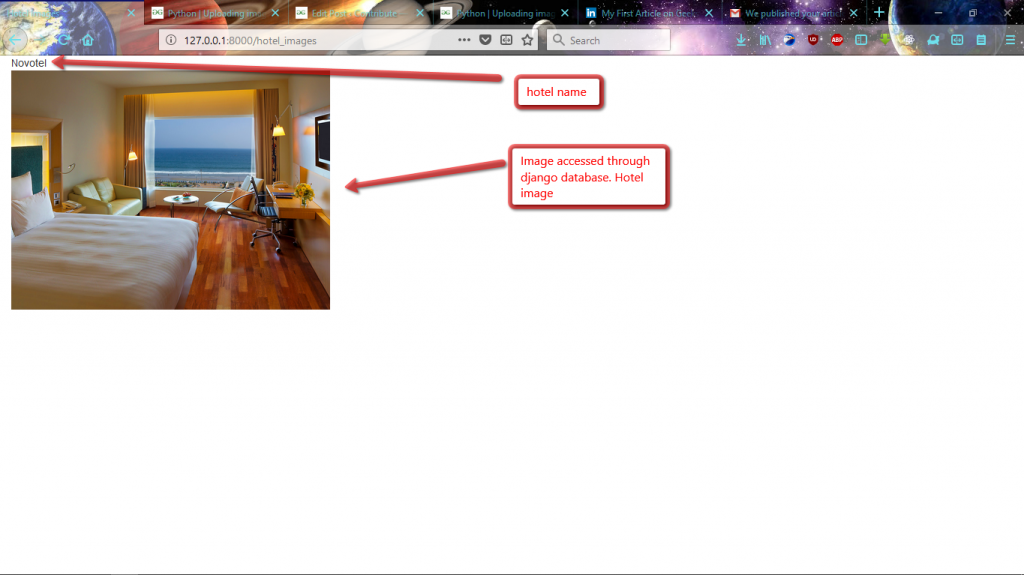
Hotel Epitome
escobedotrind1988.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python-uploading-images-in-django/
0 Response to "Upload Images to Django Using Put Request"
Post a Comment